NBFC Registration

NBFCs or Non-Banking Financial Company are registered under the Companies Act 1956/Companies Act 2013. Though these do not possess a banking license, yet are involved in various financial services. Some of the services include:
- Loan and credit facilities
- Asset Financing
- Acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds
- Hire-purchase
- Insurance business
- Chit business
- Currency exchange
- Peer to peer lending
- Hedge funds
What is not included under NBFCs?

And if the company is engaged in other activities, then it is not registered as an NBFC. Some of the activities are:
- Agriculture activity
- Industrial activity
- Purchase/sale of any goods
- Providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of the immovable property
Classification of NBFC
The classification based on authorization to take deposits:
- Type-1: Deposit-taking (NBFC-D)
- Type-2: Non-deposit taking (NBFC-ND)
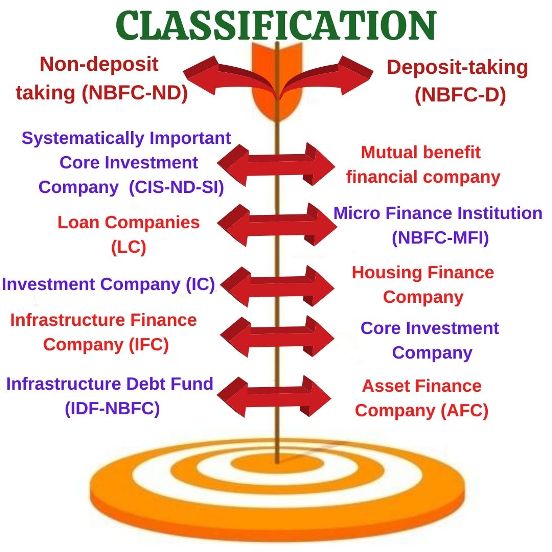
The classification based on their activities:
Asset Finance Company (AFC): If the primary business of the company is to finance the assets of a firm, such as machines, automobiles, generators, material equipment, industrial machines, etc. it is called Asset Finance Company.
Investment Company (IC): These companies deal primarily in securities.
Loan Companies (LC): The main business for these companies is to grant loans and advances. These loans are not for asset acquisition, but other purposes, such as working capital finance, etc.
Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): The companies falling under this category owns at least Rs.300 Crore and deploys 75% of its total assets in infrastructure loans. It must also have credit rating A or above and CRAR of 15%.
Systematically Important Core Investment Company: In case a company owns assets worth Rs.100 crore or more and has deployed 90% of its assets in debt instruments or loans in group companies, then it is considered as CIS-ND-SI. Of the 90%, 90% should be invested in equity shares.
Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF-NBFC): The investment of these companies is primarily in the infrastructure sector. These funds are crucial, as it is difficult to obtain these funds. It is because of its scale of the requirement of these funds, long gestation period and long-term requirements.
You could either register this as a trust or a company.
In case it’s a trust, then it would be a mutual fund which comes under SEBI regulations. It will then be called as IDF-MF.
And if it is a company, then it would be under RBI regulations. Then it will be called as IDF-NBFC.
Mutual benefit financial company: This is a type of company, whose main aim is to enable its members to pool their money with a pre-calculated investment objectives. The sources of this fund are share capital & deposits from its members and the general public.
Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI): This is a non-deposit taking NBFC that has at least 85% of its assets in the form of microfinance.
Housing Finance Company: In the Memorandum of Association of these companies, there is a clause of housing finance mentioned. These provide mid-term capital loans to individuals or firms. Due to its less stringent regulations and flexibility, these companies are a much better alternative to commercial banks.
Core Investment Company: These are the business company that conducts the business of acquisition of securities and shares, these companies hold 90% of its asset in the form of bonds, equity shares, and preference shares. Also, these companies need to invest at least 60% in equity shares.
Regulations of NBFC
| Company Type | Regulators |
| NBFCs registered with RBI | Regulation, supervision, surveillance and enforcement under RBI |
| NBFC regulated by other regulators | Depends on the type of institution |
| Housing Finance Institutions | National Housing Bank |
| Merchant Banking Company/Venture Capital Fund Company/Stock Broking/Collective Investment Schemes (CIS) | Securities Exchange Board of India |
| Nidhi Companies and Mutual Benefit Companies | Ministry of Corporate Affairs |
| Chit Fund Companies | State Government |
| Insurance Companies | Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority |
| Non-Banking Non-Finance Companies | Regulation, supervision, surveillance and enforcement under the Companies Act 1956. |
Pre-requirements of NBFC

For a company to be considered an NBFC, it should be registered as per the rules, regulations, and provisions mentioned in the Companies Act 2013 of the Companies Act 1956.
The minimum owned fund for this should be Rs.2 crore and this shouldn’t be borrowed fund. (This limit is different in other cases like that of specialized NBFCs like NBFC-MFIs, NBFC Factors, CICs, as it is decided on the kind of NBFC). Any gift from spouse comes under owned-funds.
At least 1/3rd of the directors must have some experience in finance.
Also, there must be a detailed plan for the next 5 years.
NBFCs as sponsors of IDF-MF
For a company to be considered as IDF-MF, the minimum owned fund should be at least Rs.3 crore, CRAR of 15% and NPA not more than 3% of the net advances. Along with this, the company should be operational for the last 5 years and profitable in the last 3 years.
NBFC Registration Fees
The government charges Rs.3,50,000 approx. And adding this to the professional fees could bring the total amount to Rs.15 lakh. But, if you use our services, it would cost you Rs.6,00,000 + Government fees for the registration.
Documents Required for NBFC Registration

Significant documents required for NBFC Registration in India are as follows:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Documents related to the administration and management of the company
- Company Incorporation Certificate
- The Memorandum of Association and the Articles of Association of the applicant-company or firm
- Documents describing the location of the company
- Detailed information about Directors or Partners of the Company
- Accounts of the company well-audited for last three consecutive years
- Board Resolution in favor of NBFC formation
- Should have a bank Account with a minimum paid up equity share capital of INR-2 Crore
- Income tax PAN, etc.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Advantages

- NBFCs can provide loan and credit facilities to its clients
- These companies can also trade in money market instruments.
- The NBFCs can also take part in wealth management such as managing a portfolio of stocks and shares.
- These companies become the last resort for many other businesses as these are pumping huge amounts of money in country-wide projects.
- The functioning of these companies is much faster than banks.
- Due to the use of technological advancements, you don’t have to depend on bank branches.
- Due to its digitization, the reach of the NBFCs has broadened and it can reach a wider audience within seconds.
- Investments in property with NBFCs are profitable due to its flexible rates, easy repayment, acceptable property collaterals with quick and easy processing.
- Most of the NBFCs have formed partnerships with the government and used their database and identify customer worthiness before granting loans. This would reduce the risks and maximize profits.
Role of NBFCs
NBFCs can lend both secured and unsecured loans based on their alternative lending models. These companies play a significant role in the financial services of the economy and have gone considerable changes in recent years. And after adopting high-end tech-based business models, the roles offered by them are:
- NBFCs create a favorable balance in the financial needs of the country as most of the applications are rejected by the traditional banks.
- These companies use alternative credit scoring model to assess the potential client and after this process the loans.
- Most of the Indian Fin-tech companies have been using the NBFC model to offer financial services.

